4.1 Kubelet 主对象构建和状态函数设置机制
NewMainKubelet()是 kubelet 对象的工厂方法,实现了复杂的依赖注入和组件初始化。它采用构造器模式,分阶段初始化各个组件:配置验证、信息收集器创建、运行时管理器构建、PLEG 初始化等。最后设置setNodeStatusFuncs将所有状态设置函数绑定到 kubelet 对象,这种延迟绑定的设计确保了所有依赖组件都已正确初始化。健康检查的注册(addHealthCheck )将 PLEG 纳入运行时状态监控体系。
在创建kubelet对象时,通过klet.setNodeStatusFuncs = klet.defaultNodeStatusFuncs()将defaultNodeStatusFuncs()赋值给了klet.setNodeStatusFuncs ,后续在上报状态时通过这个函数设置节点状态。
func NewMainKubelet(kubeCfg *kubeletconfiginternal.KubeletConfiguration,
kubeDeps *Dependencies,
crOptions *config.ContainerRuntimeOptions,
containerRuntime string,
hostname string,
hostnameOverridden bool,
nodeName types.NodeName,
nodeIPs []net.IP,
providerID string,
cloudProvider string,
certDirectory string,
rootDirectory string,
imageCredentialProviderConfigFile string,
imageCredentialProviderBinDir string,
registerNode bool,
registerWithTaints []api.Taint,
allowedUnsafeSysctls []string,
experimentalMounterPath string,
kernelMemcgNotification bool,
experimentalCheckNodeCapabilitiesBeforeMount bool,
experimentalNodeAllocatableIgnoreEvictionThreshold bool,
minimumGCAge metav1.Duration,
maxPerPodContainerCount int32,
maxContainerCount int32,
masterServiceNamespace string,
registerSchedulable bool,
keepTerminatedPodVolumes bool,
nodeLabels map[string]string,
seccompProfileRoot string,
nodeStatusMaxImages int32) (*Kubelet, error) {
if rootDirectory == "" {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid root directory %q", rootDirectory)
}
if kubeCfg.SyncFrequency.Duration <= 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid sync frequency %d", kubeCfg.SyncFrequency.Duration)
}
if kubeCfg.MakeIPTablesUtilChains {
if kubeCfg.IPTablesMasqueradeBit > 31 || kubeCfg.IPTablesMasqueradeBit < 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("iptables-masquerade-bit is not valid. Must be within [0, 31]")
}
if kubeCfg.IPTablesDropBit > 31 || kubeCfg.IPTablesDropBit < 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("iptables-drop-bit is not valid. Must be within [0, 31]")
}
if kubeCfg.IPTablesDropBit == kubeCfg.IPTablesMasqueradeBit {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("iptables-masquerade-bit and iptables-drop-bit must be different")
}
}
var nodeHasSynced cache.InformerSynced
var nodeLister corelisters.NodeLister
// If kubeClient == nil, we are running in standalone mode (i.e. no API servers)
// If not nil, we are running as part of a cluster and should sync w/API
if kubeDeps.KubeClient != nil {
kubeInformers := informers.NewSharedInformerFactoryWithOptions(kubeDeps.KubeClient, 0, informers.WithTweakListOptions(func(options *metav1.ListOptions) {
options.FieldSelector = fields.Set{api.ObjectNameField: string(nodeName)}.String()
}))
nodeLister = kubeInformers.Core().V1().Nodes().Lister()
nodeHasSynced = func() bool {
return kubeInformers.Core().V1().Nodes().Informer().HasSynced()
}
kubeInformers.Start(wait.NeverStop)
klog.Info("Attempting to sync node with API server")
} else {
// we don't have a client to sync!
nodeIndexer := cache.NewIndexer(cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc, cache.Indexers{})
nodeLister = corelisters.NewNodeLister(nodeIndexer)
nodeHasSynced = func() bool { return true }
klog.Info("Kubelet is running in standalone mode, will skip API server sync")
}
if kubeDeps.PodConfig == nil {
var err error
kubeDeps.PodConfig, err = makePodSourceConfig(kubeCfg, kubeDeps, nodeName, nodeHasSynced)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
containerGCPolicy := kubecontainer.GCPolicy{
MinAge: minimumGCAge.Duration,
MaxPerPodContainer: int(maxPerPodContainerCount),
MaxContainers: int(maxContainerCount),
}
daemonEndpoints := &v1.NodeDaemonEndpoints{
KubeletEndpoint: v1.DaemonEndpoint{Port: kubeCfg.Port},
}
imageGCPolicy := images.ImageGCPolicy{
MinAge: kubeCfg.ImageMinimumGCAge.Duration,
HighThresholdPercent: int(kubeCfg.ImageGCHighThresholdPercent),
LowThresholdPercent: int(kubeCfg.ImageGCLowThresholdPercent),
}
enforceNodeAllocatable := kubeCfg.EnforceNodeAllocatable
if experimentalNodeAllocatableIgnoreEvictionThreshold {
// Do not provide kubeCfg.EnforceNodeAllocatable to eviction threshold parsing if we are not enforcing Evictions
enforceNodeAllocatable = []string{}
}
thresholds, err := eviction.ParseThresholdConfig(enforceNodeAllocatable, kubeCfg.EvictionHard, kubeCfg.EvictionSoft, kubeCfg.EvictionSoftGracePeriod, kubeCfg.EvictionMinimumReclaim)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
evictionConfig := eviction.Config{
PressureTransitionPeriod: kubeCfg.EvictionPressureTransitionPeriod.Duration,
MaxPodGracePeriodSeconds: int64(kubeCfg.EvictionMaxPodGracePeriod),
Thresholds: thresholds,
KernelMemcgNotification: kernelMemcgNotification,
PodCgroupRoot: kubeDeps.ContainerManager.GetPodCgroupRoot(),
}
var serviceLister corelisters.ServiceLister
var serviceHasSynced cache.InformerSynced
if kubeDeps.KubeClient != nil {
kubeInformers := informers.NewSharedInformerFactory(kubeDeps.KubeClient, 0)
serviceLister = kubeInformers.Core().V1().Services().Lister()
serviceHasSynced = kubeInformers.Core().V1().Services().Informer().HasSynced
kubeInformers.Start(wait.NeverStop)
} else {
serviceIndexer := cache.NewIndexer(cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc, cache.Indexers{cache.NamespaceIndex: cache.MetaNamespaceIndexFunc})
serviceLister = corelisters.NewServiceLister(serviceIndexer)
serviceHasSynced = func() bool { return true }
}
// construct a node reference used for events
nodeRef := &v1.ObjectReference{
Kind: "Node",
Name: string(nodeName),
UID: types.UID(nodeName),
Namespace: "",
}
oomWatcher, err := oomwatcher.NewWatcher(kubeDeps.Recorder)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
clusterDNS := make([]net.IP, 0, len(kubeCfg.ClusterDNS))
for _, ipEntry := range kubeCfg.ClusterDNS {
ip := net.ParseIP(ipEntry)
if ip == nil {
klog.Warningf("Invalid clusterDNS ip '%q'", ipEntry)
} else {
clusterDNS = append(clusterDNS, ip)
}
}
httpClient := &http.Client{}
klet := &Kubelet{
hostname: hostname,
hostnameOverridden: hostnameOverridden,
nodeName: nodeName,
kubeClient: kubeDeps.KubeClient,
heartbeatClient: kubeDeps.HeartbeatClient,
onRepeatedHeartbeatFailure: kubeDeps.OnHeartbeatFailure,
rootDirectory: rootDirectory,
resyncInterval: kubeCfg.SyncFrequency.Duration,
sourcesReady: config.NewSourcesReady(kubeDeps.PodConfig.SeenAllSources),
registerNode: registerNode,
registerWithTaints: registerWithTaints,
registerSchedulable: registerSchedulable,
dnsConfigurer: dns.NewConfigurer(kubeDeps.Recorder, nodeRef, nodeIPs, clusterDNS, kubeCfg.ClusterDomain, kubeCfg.ResolverConfig),
serviceLister: serviceLister,
serviceHasSynced: serviceHasSynced,
nodeLister: nodeLister,
nodeHasSynced: nodeHasSynced,
masterServiceNamespace: masterServiceNamespace,
streamingConnectionIdleTimeout: kubeCfg.StreamingConnectionIdleTimeout.Duration,
recorder: kubeDeps.Recorder,
cadvisor: kubeDeps.CAdvisorInterface,
cloud: kubeDeps.Cloud,
externalCloudProvider: cloudprovider.IsExternal(cloudProvider),
providerID: providerID,
nodeRef: nodeRef,
nodeLabels: nodeLabels,
nodeStatusUpdateFrequency: kubeCfg.NodeStatusUpdateFrequency.Duration,
nodeStatusReportFrequency: kubeCfg.NodeStatusReportFrequency.Duration,
os: kubeDeps.OSInterface,
oomWatcher: oomWatcher,
cgroupsPerQOS: kubeCfg.CgroupsPerQOS,
cgroupRoot: kubeCfg.CgroupRoot,
mounter: kubeDeps.Mounter,
hostutil: kubeDeps.HostUtil,
subpather: kubeDeps.Subpather,
maxPods: int(kubeCfg.MaxPods),
podsPerCore: int(kubeCfg.PodsPerCore),
syncLoopMonitor: atomic.Value{},
daemonEndpoints: daemonEndpoints,
containerManager: kubeDeps.ContainerManager,
containerRuntimeName: containerRuntime,
nodeIPs: nodeIPs,
nodeIPValidator: validateNodeIP,
clock: clock.RealClock{},
enableControllerAttachDetach: kubeCfg.EnableControllerAttachDetach,
makeIPTablesUtilChains: kubeCfg.MakeIPTablesUtilChains,
iptablesMasqueradeBit: int(kubeCfg.IPTablesMasqueradeBit),
iptablesDropBit: int(kubeCfg.IPTablesDropBit),
experimentalHostUserNamespaceDefaulting: utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.ExperimentalHostUserNamespaceDefaultingGate),
keepTerminatedPodVolumes: keepTerminatedPodVolumes,
nodeStatusMaxImages: nodeStatusMaxImages,
lastContainerStartedTime: newTimeCache(),
}
if klet.cloud != nil {
klet.cloudResourceSyncManager = cloudresource.NewSyncManager(klet.cloud, nodeName, klet.nodeStatusUpdateFrequency)
}
var secretManager secret.Manager
var configMapManager configmap.Manager
switch kubeCfg.ConfigMapAndSecretChangeDetectionStrategy {
case kubeletconfiginternal.WatchChangeDetectionStrategy:
secretManager = secret.NewWatchingSecretManager(kubeDeps.KubeClient)
configMapManager = configmap.NewWatchingConfigMapManager(kubeDeps.KubeClient)
case kubeletconfiginternal.TTLCacheChangeDetectionStrategy:
secretManager = secret.NewCachingSecretManager(
kubeDeps.KubeClient, manager.GetObjectTTLFromNodeFunc(klet.GetNode))
configMapManager = configmap.NewCachingConfigMapManager(
kubeDeps.KubeClient, manager.GetObjectTTLFromNodeFunc(klet.GetNode))
case kubeletconfiginternal.GetChangeDetectionStrategy:
secretManager = secret.NewSimpleSecretManager(kubeDeps.KubeClient)
configMapManager = configmap.NewSimpleConfigMapManager(kubeDeps.KubeClient)
default:
return nil, fmt.Errorf("unknown configmap and secret manager mode: %v", kubeCfg.ConfigMapAndSecretChangeDetectionStrategy)
}
klet.secretManager = secretManager
klet.configMapManager = configMapManager
if klet.experimentalHostUserNamespaceDefaulting {
klog.Infof("Experimental host user namespace defaulting is enabled.")
}
machineInfo, err := klet.cadvisor.MachineInfo()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Avoid collector collects it as a timestamped metric
// See PR #95210 and #97006 for more details.
machineInfo.Timestamp = time.Time{}
klet.setCachedMachineInfo(machineInfo)
imageBackOff := flowcontrol.NewBackOff(backOffPeriod, MaxContainerBackOff)
klet.livenessManager = proberesults.NewManager()
klet.startupManager = proberesults.NewManager()
klet.podCache = kubecontainer.NewCache()
// podManager is also responsible for keeping secretManager and configMapManager contents up-to-date.
mirrorPodClient := kubepod.NewBasicMirrorClient(klet.kubeClient, string(nodeName), nodeLister)
klet.podManager = kubepod.NewBasicPodManager(mirrorPodClient, secretManager, configMapManager)
klet.statusManager = status.NewManager(klet.kubeClient, klet.podManager, klet)
klet.resourceAnalyzer = serverstats.NewResourceAnalyzer(klet, kubeCfg.VolumeStatsAggPeriod.Duration)
klet.dockerLegacyService = kubeDeps.dockerLegacyService
klet.runtimeService = kubeDeps.RemoteRuntimeService
if kubeDeps.KubeClient != nil {
klet.runtimeClassManager = runtimeclass.NewManager(kubeDeps.KubeClient)
}
if containerRuntime == kubetypes.RemoteContainerRuntime && utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.CRIContainerLogRotation) {
// setup containerLogManager for CRI container runtime
containerLogManager, err := logs.NewContainerLogManager(
klet.runtimeService,
kubeDeps.OSInterface,
kubeCfg.ContainerLogMaxSize,
int(kubeCfg.ContainerLogMaxFiles),
)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to initialize container log manager: %v", err)
}
klet.containerLogManager = containerLogManager
} else {
klet.containerLogManager = logs.NewStubContainerLogManager()
}
runtime, err := kuberuntime.NewKubeGenericRuntimeManager(
kubecontainer.FilterEventRecorder(kubeDeps.Recorder),
klet.livenessManager,
klet.startupManager,
seccompProfileRoot,
machineInfo,
klet,
kubeDeps.OSInterface,
klet,
httpClient,
imageBackOff,
kubeCfg.SerializeImagePulls,
float32(kubeCfg.RegistryPullQPS),
int(kubeCfg.RegistryBurst),
imageCredentialProviderConfigFile,
imageCredentialProviderBinDir,
kubeCfg.CPUCFSQuota,
kubeCfg.CPUCFSQuotaPeriod,
kubeDeps.RemoteRuntimeService,
kubeDeps.RemoteImageService,
kubeDeps.ContainerManager.InternalContainerLifecycle(),
kubeDeps.dockerLegacyService,
klet.containerLogManager,
klet.runtimeClassManager,
)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
klet.containerRuntime = runtime
klet.streamingRuntime = runtime
klet.runner = runtime
runtimeCache, err := kubecontainer.NewRuntimeCache(klet.containerRuntime)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
klet.runtimeCache = runtimeCache
if kubeDeps.useLegacyCadvisorStats {
klet.StatsProvider = stats.NewCadvisorStatsProvider(
klet.cadvisor,
klet.resourceAnalyzer,
klet.podManager,
klet.runtimeCache,
klet.containerRuntime,
klet.statusManager)
} else {
klet.StatsProvider = stats.NewCRIStatsProvider(
klet.cadvisor,
klet.resourceAnalyzer,
klet.podManager,
klet.runtimeCache,
kubeDeps.RemoteRuntimeService,
kubeDeps.RemoteImageService,
stats.NewLogMetricsService(),
kubecontainer.RealOS{})
}
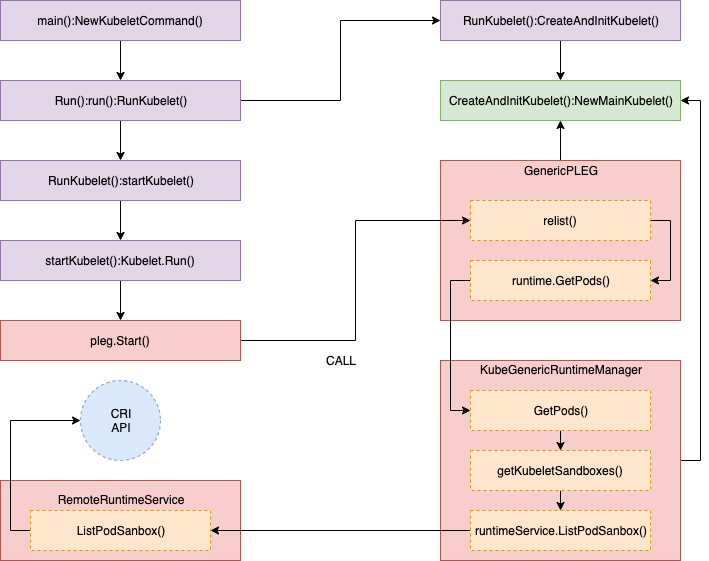
klet.pleg = pleg.NewGenericPLEG(klet.containerRuntime, plegChannelCapacity, plegRelistPeriod, klet.podCache, clock.RealClock{})
klet.runtimeState = newRuntimeState(maxWaitForContainerRuntime)
klet.runtimeState.addHealthCheck("PLEG", klet.pleg.Healthy)
if _, err := klet.updatePodCIDR(kubeCfg.PodCIDR); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Pod CIDR update failed %v", err)
}
// setup containerGC
containerGC, err := kubecontainer.NewContainerGC(klet.containerRuntime, containerGCPolicy, klet.sourcesReady)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
klet.containerGC = containerGC
klet.containerDeletor = newPodContainerDeletor(klet.containerRuntime, integer.IntMax(containerGCPolicy.MaxPerPodContainer, minDeadContainerInPod))
// setup imageManager
imageManager, err := images.NewImageGCManager(klet.containerRuntime, klet.StatsProvider, kubeDeps.Recorder, nodeRef, imageGCPolicy, crOptions.PodSandboxImage)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to initialize image manager: %v", err)
}
klet.imageManager = imageManager
if kubeCfg.ServerTLSBootstrap && kubeDeps.TLSOptions != nil && utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.RotateKubeletServerCertificate) {
klet.serverCertificateManager, err = kubeletcertificate.NewKubeletServerCertificateManager(klet.kubeClient, kubeCfg, klet.nodeName, klet.getLastObservedNodeAddresses, certDirectory)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to initialize certificate manager: %v", err)
}
kubeDeps.TLSOptions.Config.GetCertificate = func(*tls.ClientHelloInfo) (*tls.Certificate, error) {
cert := klet.serverCertificateManager.Current()
if cert == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("no serving certificate available for the kubelet")
}
return cert, nil
}
}
klet.probeManager = prober.NewManager(
klet.statusManager,
klet.livenessManager,
klet.startupManager,
klet.runner,
kubeDeps.Recorder)
tokenManager := token.NewManager(kubeDeps.KubeClient)
// NewInitializedVolumePluginMgr initializes some storageErrors on the Kubelet runtimeState (in csi_plugin.go init)
// which affects node ready status. This function must be called before Kubelet is initialized so that the Node
// ReadyState is accurate with the storage state.
klet.volumePluginMgr, err =
NewInitializedVolumePluginMgr(klet, secretManager, configMapManager, tokenManager, kubeDeps.VolumePlugins, kubeDeps.DynamicPluginProber)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
klet.pluginManager = pluginmanager.NewPluginManager(
klet.getPluginsRegistrationDir(), /* sockDir */
kubeDeps.Recorder,
)
// If the experimentalMounterPathFlag is set, we do not want to
// check node capabilities since the mount path is not the default
if len(experimentalMounterPath) != 0 {
experimentalCheckNodeCapabilitiesBeforeMount = false
// Replace the nameserver in containerized-mounter's rootfs/etc/resolve.conf with kubelet.ClusterDNS
// so that service name could be resolved
klet.dnsConfigurer.SetupDNSinContainerizedMounter(experimentalMounterPath)
}
// setup volumeManager
klet.volumeManager = volumemanager.NewVolumeManager(
kubeCfg.EnableControllerAttachDetach,
nodeName,
klet.podManager,
klet.statusManager,
klet.kubeClient,
klet.volumePluginMgr,
klet.containerRuntime,
kubeDeps.Mounter,
kubeDeps.HostUtil,
klet.getPodsDir(),
kubeDeps.Recorder,
experimentalCheckNodeCapabilitiesBeforeMount,
keepTerminatedPodVolumes,
volumepathhandler.NewBlockVolumePathHandler())
klet.reasonCache = NewReasonCache()
klet.workQueue = queue.NewBasicWorkQueue(klet.clock)
klet.podWorkers = newPodWorkers(klet.syncPod, kubeDeps.Recorder, klet.workQueue, klet.resyncInterval, backOffPeriod, klet.podCache)
klet.backOff = flowcontrol.NewBackOff(backOffPeriod, MaxContainerBackOff)
klet.podKiller = NewPodKiller(klet)
etcHostsPathFunc := func(podUID types.UID) string { return getEtcHostsPath(klet.getPodDir(podUID)) }
// setup eviction manager
evictionManager, evictionAdmitHandler := eviction.NewManager(klet.resourceAnalyzer, evictionConfig, killPodNow(klet.podWorkers, kubeDeps.Recorder), klet.podManager.GetMirrorPodByPod, klet.imageManager, klet.containerGC, kubeDeps.Recorder, nodeRef, klet.clock, etcHostsPathFunc)
klet.evictionManager = evictionManager
klet.admitHandlers.AddPodAdmitHandler(evictionAdmitHandler)
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.Sysctls) {
// Safe, whitelisted sysctls can always be used as unsafe sysctls in the spec.
// Hence, we concatenate those two lists.
safeAndUnsafeSysctls := append(sysctlwhitelist.SafeSysctlWhitelist(), allowedUnsafeSysctls...)
sysctlsWhitelist, err := sysctl.NewWhitelist(safeAndUnsafeSysctls)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
klet.admitHandlers.AddPodAdmitHandler(sysctlsWhitelist)
}
// enable active deadline handler
activeDeadlineHandler, err := newActiveDeadlineHandler(klet.statusManager, kubeDeps.Recorder, klet.clock)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
klet.AddPodSyncLoopHandler(activeDeadlineHandler)
klet.AddPodSyncHandler(activeDeadlineHandler)
klet.admitHandlers.AddPodAdmitHandler(klet.containerManager.GetAllocateResourcesPodAdmitHandler())
criticalPodAdmissionHandler := preemption.NewCriticalPodAdmissionHandler(klet.GetActivePods, killPodNow(klet.podWorkers, kubeDeps.Recorder), kubeDeps.Recorder)
klet.admitHandlers.AddPodAdmitHandler(lifecycle.NewPredicateAdmitHandler(klet.getNodeAnyWay, criticalPodAdmissionHandler, klet.containerManager.UpdatePluginResources))
// apply functional Option's
for _, opt := range kubeDeps.Options {
opt(klet)
}
if sysruntime.GOOS == "linux" {
// AppArmor is a Linux kernel security module and it does not support other operating systems.
klet.appArmorValidator = apparmor.NewValidator(containerRuntime)
klet.softAdmitHandlers.AddPodAdmitHandler(lifecycle.NewAppArmorAdmitHandler(klet.appArmorValidator))
}
klet.softAdmitHandlers.AddPodAdmitHandler(lifecycle.NewNoNewPrivsAdmitHandler(klet.containerRuntime))
klet.softAdmitHandlers.AddPodAdmitHandler(lifecycle.NewProcMountAdmitHandler(klet.containerRuntime))
leaseDuration := time.Duration(kubeCfg.NodeLeaseDurationSeconds) * time.Second
renewInterval := time.Duration(float64(leaseDuration) * nodeLeaseRenewIntervalFraction)
klet.nodeLeaseController = lease.NewController(
klet.clock,
klet.heartbeatClient,
string(klet.nodeName),
kubeCfg.NodeLeaseDurationSeconds,
klet.onRepeatedHeartbeatFailure,
renewInterval,
v1.NamespaceNodeLease,
util.SetNodeOwnerFunc(klet.heartbeatClient, string(klet.nodeName)))
// setup node shutdown manager
shutdownManager, shutdownAdmitHandler := nodeshutdown.NewManager(klet.GetActivePods, killPodNow(klet.podWorkers, kubeDeps.Recorder), klet.syncNodeStatus, kubeCfg.ShutdownGracePeriod.Duration, kubeCfg.ShutdownGracePeriodCriticalPods.Duration)
klet.shutdownManager = shutdownManager
klet.admitHandlers.AddPodAdmitHandler(shutdownAdmitHandler)
// Finally, put the most recent version of the config on the Kubelet, so
// people can see how it was configured.
klet.kubeletConfiguration = *kubeCfg
// Generating the status funcs should be the last thing we do,
// since this relies on the rest of the Kubelet having been constructed.
klet.setNodeStatusFuncs = klet.defaultNodeStatusFuncs()
return klet, nil
}